Direwolf is a powerful software TNC (Terminal Node Controller). From the Direwolf github:
Dire Wolf is a modern software replacement for the old 1980’s style TNC built with special hardware.
Without any additional software, it can perform as:
- APRS GPS Tracker
- Digipeater
- Internet Gateway (IGate)
- APRStt gateway
It can also be used as a virtual TNC for other applications such as APRSIS32, Xastir, APRS-TW, YAAC, PinPoint APRS, UI-View32,UISS, Linux AX25, SARTrack, Winlink Express (formerly known as RMS Express, formerly known as Winlink 2000 or WL2K), BPQ32, Outpost PM, Ham Radio of Things, Packet Compressed Sensing Imaging (PCSI), and many others.
In the previous post we discussed installing Direwolf. Now we need to configure Direwolf to work with our sound card and radio.
Direwolf’s documentation is stellar and can be found on their github. (https://github.com/wb2osz/direwolf/blob/master/doc/User-Guide.pdf)
I’ll do my best to summarize for our packet radio purposes. First we’ll need to edit the config file, direwolf.conf, using the text editor of your choice. This file can be found in your home directory. The config file has plenty of commented code so you know exactly what you are looking at. In short we need to edit the sound card, callsign, and method of PTT.
Use the command “arecord -l” to list your sound card
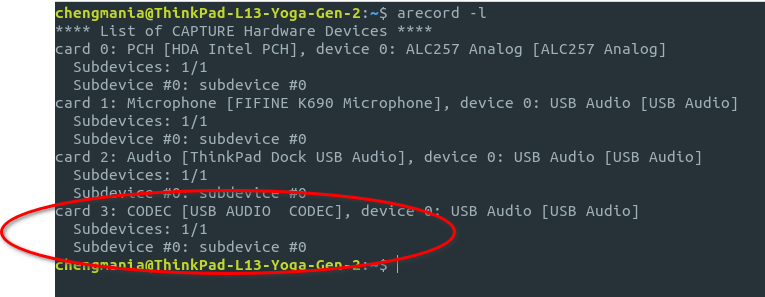
As you see in my example, my sound card is card 3, which is a Signalink. Using the nano editor we will open direwolf.conf
nano direwolf.confScroll until you see ADEVICE plughw: 0,0 and change it to the number of your soundcard device.
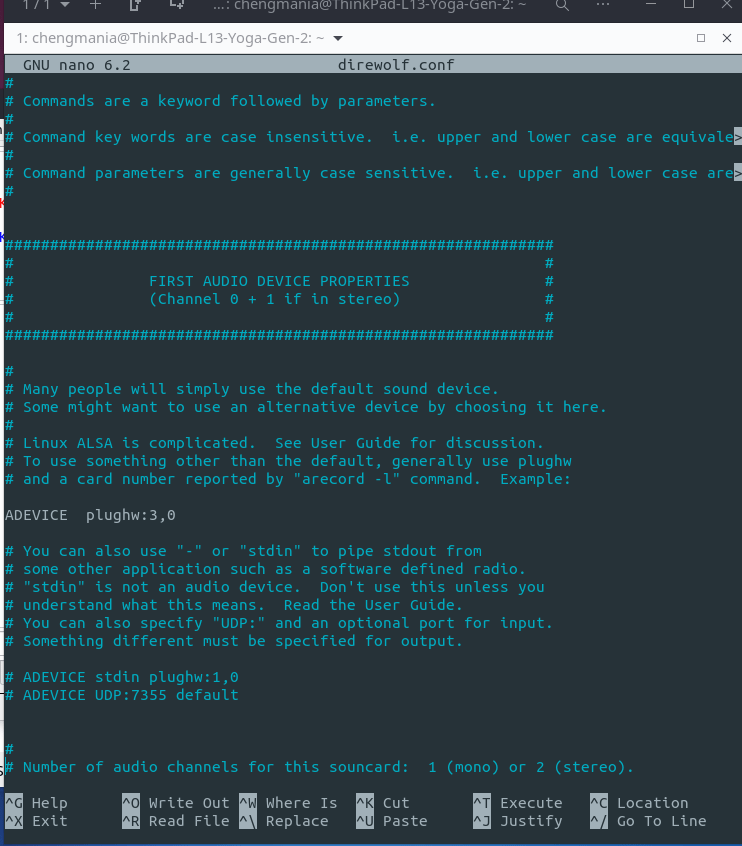
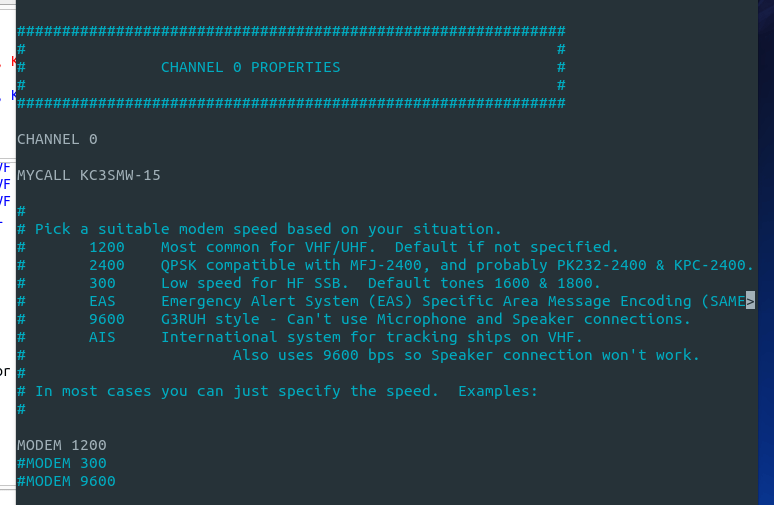
Now your sound card is set. Next scroll until you see N0CALL next to MYCALL and change it to your callsign. I recommend adding an SSID, so that the virtual TNC doesn’t share the same callsign as yourself. And choose your modem speed. For VHF Packet 1200, for HF 300.
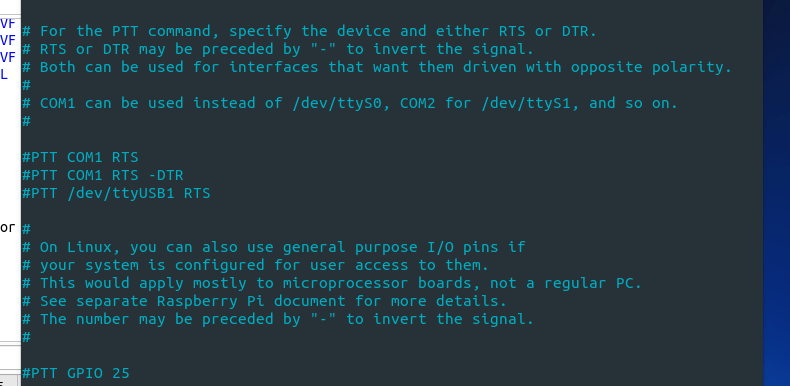
And finally PTT method. Since I am using a Signalink, which is controlled by VOX, I have no PTT method. If you are using a built in soundcard, Digirig, or Masters Communication’s DRA device, you will want to determine the USB port and RTS vs DTS method. Uncomment and modify the PTT line.
Lastly you’ll need to note the AGWPORT and KISSPORT for other software use.

Now save and exit using CRTL-X and follow the prompts at the bottom of the screen.